- Mar 16, 2024
- 8 min read
Cloud vs On-Premise Software: What to Choose for Your Business
BI & Big Data services

Vitalii Samofal
CTO
Cloud software and services are more popular than ever. Around 50% of business data is in the cloud. Experts believe that by 2025, half of all world data will be in the cloud. This is around 100 zettabytes. Yet, for many companies, on-site software is a better choice.
In this article, we will
– explain the pros and cons of cloud vs. on-premise software,
– discuss which situations call for their use and
– explore the hybrid approach as a third option.
Cloud-based software definition
Cloud-based software is any software that runs in the cloud. You need the internet to access a cloud app. Examples are Gmail, Google Docs, Slack, Salesforce, Zoho Cliq, Zoom and Trello. More than 90% of organizations worldwide use cloud solutions.
Cloud solutions became more popular because of the COVID-19 pandemic. Companies had to offer online work options. So they started using cloud software for communication and cooperation. Cloud technologies improve flexibility, scalability and cost-efficiency.
On-premise software definition
On-site software runs on personal computers or company servers. Examples are Microsoft Word, PowerPoint, VLC media player and 7-Zip.
The sales of on-site software are growing. There was a survey of 405 software development companies from 5 continents. 92% said that their sales of on-site software have increased.
Cloud software is useful for all industries. On-site software is best for
– the BFSI (banking, financial services and insurance) sector,
– healthcare,
– engineering,
– cybersecurity and
– government agencies.
The first reason is security concerns. The second is the need for large storage and processing power. These are expensive in the cloud.
8 key differences between cloud and on-premise software
So, both options are popular. Then, what is the difference between cloud and on-premise software? These are 8 key points:
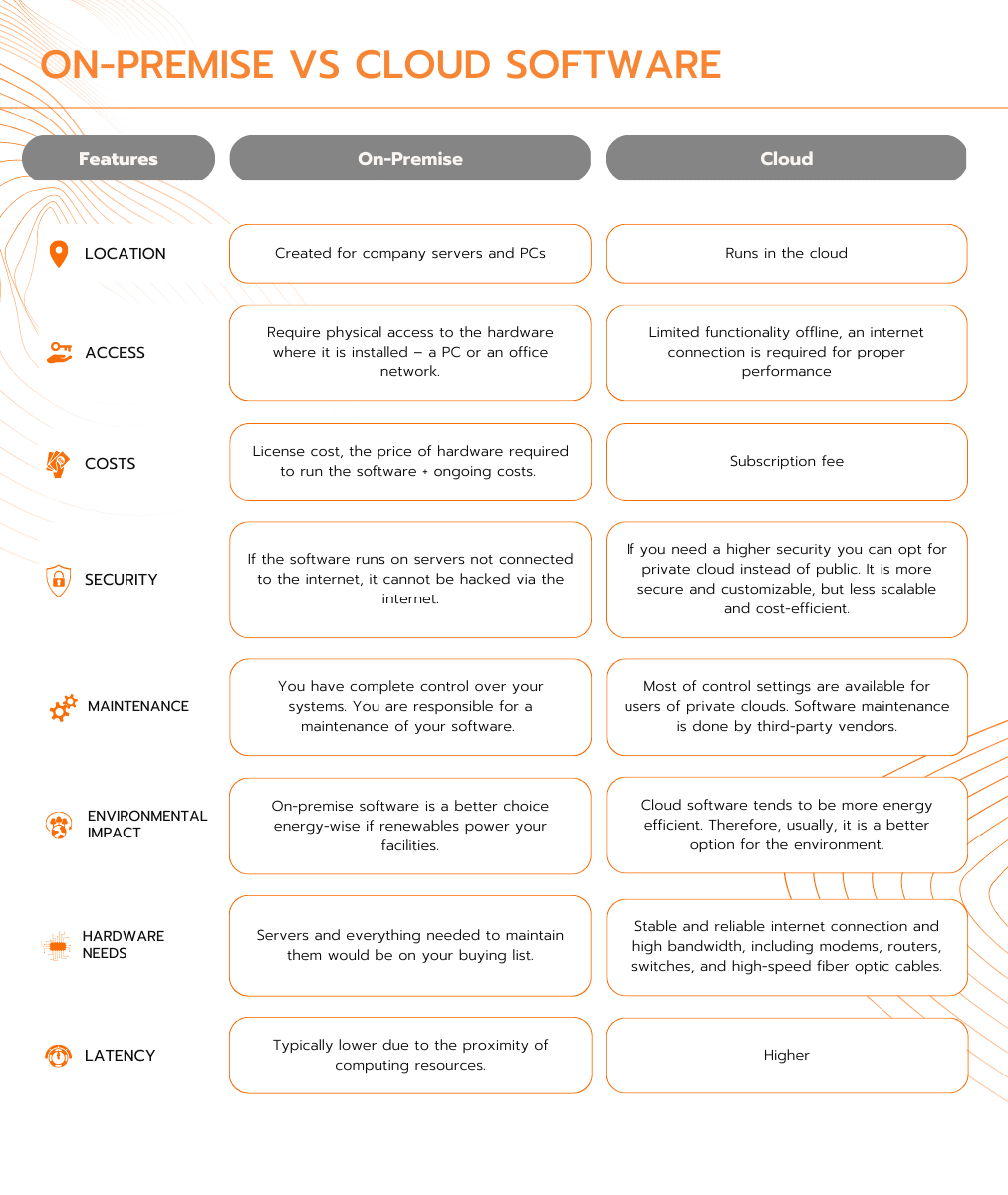
Location
As mentioned, on-site software runs on PCs and company servers. Cloud software runs in the cloud. This means that a third-party provider gives access to their hardware. The most popular cloud providers are AWS, Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud. Software built for on-site use can run in the cloud but not vice versa.
Access
Internet access is necessary for cloud software. Some cloud software can run offline. But most features wouldn't work. The internet is essential for
– real-time cooperation,
– data upload and download.
To use on-site software, workers need physical access to the on-premise hardware. This can be a PC or an office network. A company can add internet access to on-site apps. But, some don’t do it because of security reasons.
Costs
Let us compare cloud vs. on-premise costs. For this, we will analyze the software's TCO (total cost of ownership). It has two components:
Initial price
This is the price a company pays to start using the software. If the software runs on-site, it can include
– the license cost,
– the price of hardware and
– the cost of training staff to use a new app.
The initial price is higher for on-site software.
Operating costs
This is the price a business regularly pays for using the software. For on-premises apps, this includes
– hardware maintenance costs (for example, repair costs),
– energy bills and
– IT staff salary.
For ready-made cloud apps, businesses can buy
– time-based subscription licenses or
– metered licenses.
The latter means that a company buys a certain amount of services. For example, speech-to-text software often charges per hour.
To run custom software in the cloud, businesses need to buy
– cloud storage and
– computing power.
The service providers handle hardware updates and maintenance. Economies of scale make it cost-efficient for many businesses. Especially for small ones. Thus, with cloud services, a local bakery doesn't need to maintain a server room. They can use the cloud and have a nice website or off-site CRM access.
But cloud services are hard to set up right. You should have enough capacity without paying for what you don't need. Companies spend around 36% more on cloud services than they need. The good news is that businesses can avoid this. You can hire professionals to set up your cloud use. At Softkit, we have an excellent track record. Our team has helped many clients decrease their cloud costs by 20 to 40%.
Security
Security is one of the main reasons businesses choose on-site software. Let's imagine the software runs on servers. It is not connected to the internet. Then, nobody can hack it via the internet. But a company should protect the facility. No one should be able to access the servers without permission. Yet, cloud software is secure too. Even NASA uses the cloud.
Now let's imagine that an organization wants to use the cloud. But they need high security. They can rent a private cloud. Private clouds are environments dedicated to one customer. They are more secure and customizable than private clouds. But they are less scalable and cost-efficient.
When choosing between on-premise vs. private cloud, there is a lot to consider. For example, whether you can protect on-site software. If not, data is safer on the cloud vs. on-premise.
Maintenance and control
With on-site software, your team has complete control over your systems. You decide
– whether you need any upgrades,
– where to back up data,
– what operating system to use, and so on.
Yet, most of these control settings are also available on private clouds.
Companies that choose on-site software should also consider maintenance. As for cloud maintenance, service providers do it themselves.
Environment
Climate change is a huge threat to our planet. Many businesses promised to take action. So, what is the environmental effect of cloud computing vs. on-premise solutions?
Cloud computing is more energy efficient. Thus, it can be a better option. But, it is important to choose service providers who use clean energy.
If clean energy powers your facilities, on-site software is a better choice.
Hardware needs
Hardware needs for on-site software are huge. You will need servers and various maintenance tools. For cloud software, you need hardware that provides stable internet and high bandwidth. This includes modems, routers, switches and high-speed fibre optic cables.
Latency
Latency measures the time between a person requesting and receiving information. The lower the latency, the better. So, let's compare the latency of cloud storage vs. on-premise.
With on-site software, latency is lower. This is because computing resources are nearby. Some companies need to process data fast to make quick business decisions. They prefer on-site software.
The cloud offers opportunities to decrease latency for content distribution. Thus, content makers use cloud services to improve the experience for end users. For example, Netflix and Peacock use AWS CloudFront.
4 primary benefits of cloud software
The benefits of cloud vs. on-premise software include the following:
Flexibility and scalability
You can increase or decrease the processing power of cloud-based software in minutes. Most cloud providers offer autoscaling tools. They automate the process for optimal efficiency. Autoscaling solutions are cost-efficient. For example, our team set up the AWS Autoscaling tool for our client, SOLD.com. This decreased their cloud spending by 23.5%.
Cloud flexibility is great for companies with high seasonality.
Cost-efficiency
Cloud software can cost less than on-site solutions. Businesses don't need to buy and maintain costly hardware. And they take advantage of economies of scale.
Energy-efficiency
Cloud data centers are energy-efficient. They contribute to the development of a low-carbon economy.
Accessibility
Another advantage of cloud vs. on-premise software is its high accessibility. People can access cloud software from any place with an internet connection.
4 advantages of on-premise software
The top four reasons why companies choose on-site software are:
Security
Cyber attacks are on the rise. So, many businesses don't trust cloud providers with their security. On-site applications can be better protected. But companies must set strict security protocols.
Data protection
Businesses must protect sensitive data well. This includes:
– trade secrets;
– personal healthcare information and
– financial information.
Examples of protected trade secrets are
– Coca-Cola's signature drink recipe,
– KFC's blend of spices and herbs,
– Google search algorithm and so on.
Increased availability
Availability is the percentage of time when the software works. Software with high availability should have at least 99.999% uptime. Thus, its downtime shouldn't exceed 5.26 minutes yearly. So, let us compare the availability of on-premise vs. cloud computing.
Availability and disaster recovery are better in on-site software. This is because of lower latency. Downloading data via a local area network (LAN) is speedier than over the internet.
But, it is possible to achieve high availability using cloud solutions. For example, our team provided 99.9999999% uptime for our IoT Solution for Cars.
Compliance
Businesses must follow various local regulations. They control data storage and processing. Examples are:
- Local storage rules
The data or its copy must remain inside the country's borders. An example is the Swedish Bookkeeping Act. It says that some documents must remain in Sweden for 7 years. This includes businesses' annual financial reports;
- Local processing rules
This is the demand to process certain types of data within country borders;
- Bans on data transfer
Neither data nor its copy can leave the country. One example is Australia. Businesses must store and process the health data of Australians within the country’s borders. A similar situation is in Canada's provinces of British Columbia and Nova Scotia. There, public institutions must keep personal information in Canada. The rule applies to hospitals, schools, universities and governmental agencies.
- Conditional data transfer
Companies cannot transfer data unless they meet certain conditions. In the EU, businesses must meet safety standards to transfer personal data outside the EEA.
Data is subject to the laws of its origin country. Experts call this data sovereignty.
What is a hybrid cloud solution?
You do not have to choose either cloud or on-premise. You can combine public and private clouds with on-site infrastructure. Experts call it a hybrid cloud.
Thus, a company can keep sensitive data on-premises. But they can also process non-critical data in the cloud. The cloud’s scalability is especially useful during periods of high traffic.
The latest hybrid trend is workload portability. This is the ability to move workloads across cloud and on-premises environments. Microservice infrastructure is useful for this.
What is cloud migration?
Cloud migration means moving data and software into the cloud. Do you prefer the advantages of cloud vs. on-premise? Then, Softkit is happy to help you. We will make sure that this process does not disturb your working processes.
Softkit Will Help Your Business to Find The Best Solution
Softkit has huge experience in setting up on-site, cloud, and hybrid solutions. Let us provide you with several examples.
As a part of the IoT Solution for Cars, our team has:
- Provided 99.9999999% software uptime. We used several types of horizontal scaling;
- Wrote a custom script for CI/CD deployment. Now, developers can see the future costs of deploying and running new software;
- Ensured 500 msec request processing time. We used geographic load balancing, multi-region deployment and dynamic DNS.
For a leading gift retailer project, we:
- Set up data transfer from all its subsidiaries to Akeneo PIM software;
- Developed microservice architecture;
- Optimized the company's use of the Google Cloud Platform. This saves them around 40% on infrastructure costs!
When working on the real estate marketplace project, our team has:
- Set up AWS autoscaling. This feature saves the company 23.5% on its AWS costs;
- Connected the company's platform and database with Salesforce. We used Amazon SQS to make sure that company data is safe;
- Set up marketing and business analytics. We connected data from marketing channels to Amazon Redshift. There, custom Python scripts process it.
Was this cloud vs. on-premise comparison helpful? Let us know.
FAQ
Cloud vs. on-premise: what does my company need?
Choosing on-premise or cloud depends on your company's goals. Learn 8 key differences between cloud and on-premise software.
Why do many companies rely on a cloud vs. on-premise?
The advantages of cloud vs. on-premise software include increased flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. Learn more in the "4 primary benefits of cloud software" section.
Why do many companies choose on-premise vs. cloud software?
The benefits of on-premises software comprise better security and data protection, increased software availability, lower latency and the ability to comply with various local regulations regarding data sovereignty. Learn more in the "4 primary benefits of cloud software" section.
How do cloud-managed security vs. on-premise security differ?
When comparing cloud-based software vs. on-premise software, the former is widely considered to be less secure. However, companies must implement and follow strict security measures for adequate protection of on-premises applications.
Subscribe to our blog
Fill out the form below to receive a free consultation and find out how Softkit can help your business grow.